E-Commerce: The Best Models of e-Commerce and its Examples.

In the area of e-commerce, several important e-commerce business models have emerged, each representing a particular strategy for conducting online business. These models outline the buying and selling of commodities and services, as well as the participants and the connections among them. You can read my post on “What is e-commerce” to learn more about it and its benefits and drawbacks. this article will help you to understand the 8 best models of e-commerce.
8 Models of E-Commerce: Following are the eight key models of e-commerce which explain one by one in details:
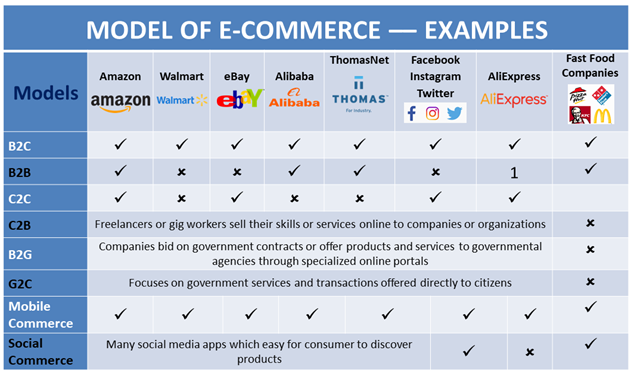
1. Business-to-Consumer (B2C):
B2C e-commerce entails dealings between companies and particular customers. In this business strategy, companies use websites or online platforms (such as Facebook, Instagram, Whatsapp, etc.) to sell goods or services directly to customers. The company manages order fulfillment and shipping as customers browse, choose, and buy products from the online store. B2C e-commerce is prevalent in online retail, where companies like following directly supply to individual consumers. Fast food companies who selling their product directly to end users is also falls in B2C model
- Companies like Amazon, Walmart, AliExpress, Drazpk etc providing platform to consumer to buy online.
- Fast food chain like KFC, Coca Cola, McDonald, Pizza and many more providing their ready product to consumer to use instantly.
- The B2C business model also includes smart phone manufacturers. These smart phone companies also fall within the B2B and B2G e-commerce models. Consider the question, “Is Apple a B2C model?” Yes, it is the answer. However, it also sells its goods to businesses, government agencies, and educational institutions.

2. Business-to-Business (B2B):
Business-to-business transactions are the focus of B2B e-commerce. Through online marketplaces, producers, wholesalers, or suppliers offer their goods or services to other companies. To meet the unique requirements of commercial customers, these platforms frequently offer cutting-edge functionality including bulk ordering, negotiated pricing, and specialized catalogs. B2B e-commerce facilitates effective supply chain management by streamlining the procurement process. ThomasNet and Alibaba is a couple of examples. Some fast food items fit under the B2B paradigm, much like Coca-Cola, which sells its goods both directly to consumers and to companies. This indicates that Coca-Cola does not directly sell these kinds of items to consumers, but rather through other outlets like tuck shops, coffee shops, etc.
3. Consumer-to-Consumer (C2C):
Individual customers can transact with one another directly through C2C e-commerce. Online markets serve as middlemen, facilitating trade and giving users a venue to post products for sale. Marketplaces on Facebook, Craigslist, and eBay are examples of popular C2C platforms. Participants in the above arrangement have the option of acting as purchasers as well as sellers, enabling people to earn money by selling their used items or their own handcrafted goods.
- Example of C2C: PayPal, Western Union and Olx etc.

4. Consumer-to-Business (C2B):
The conventional B2C concept is turned around by C2B e-commerce. Individual customers sell goods or services to businesses in this scenario. An illustration of this is when independent contractors or gig workers market their expertise or services to businesses or organizations online. Another type of C2B e-commerce is crowdsourcing platforms, where customers provide businesses ideas or designs. Another example of the C2B approach is in the small business sector.
5. Business-to-Government (B2G):
B2G e-commerce involves online transactions between businesses and government entities. Companies bid on government contracts or offer products and services to governmental agencies through specialized online portals. B2G e-commerce can streamline the procurement process for government purchases and improve transparency in government dealings.
6. Government-to-Citizen (G2C):
G2C e-commerce is focused on transactions and services provided directly to citizens. With this paradigm, citizens can use online portals to pay taxes, obtain licenses, access government data, and use a variety of public services. G2C e-commerce improves citizen convenience and government effectiveness. Electricity is the ideal example of this model. Electricity is produced by the government and sold and given directly to users. The government actively collects taxes and product costs from the general public on behalf of this service.
7. Mobile Commerce (M-Commerce):
M-commerce refers to e-commerce transactions conducted through mobile devices, such as smartphones and tablets. It encompasses all the previously mentioned models but emphasizes the use of mobile apps or mobile-optimized websites for conducting business. M-commerce has grown rapidly with the increasing adoption of mobile devices worldwide.

8. Social e-Commerce:
Social commerce integrates e-commerce with social media platforms. Businesses leverage social media channels to showcase products, engage with customers, and facilitate purchases directly within social media apps. Social commerce blurs the lines between social interactions and online shopping, making it easier for consumers to discover and buy products based on recommendations and social connections.
In an increasingly interconnected world, Social Commerce emerges as a transformative force in the e-commerce landscape. It marries the social media experience with online shopping, blurring the lines between browsing, discovering, and purchasing products.
Social Commerce is more than just a transactional process. It’s about creating a shopping journey that feels interactive and personalized. By leveraging social media platforms, businesses can tap into the power of social interactions to drive sales and create brand loyalty.
Summary of e-commerce Models:
E-commerce is an opportunity:
The potential provided by these important e-commerce models are varied for both firms and consumers, and each model calls for particular tactics, technologies, and marketing techniques. E-commerce is anticipated to experience further breakthroughs as technology develops, possibly giving rise to new hybrid models and markets. Digital marketing also plays a crucial part in the e-commerce sector. See the article “Digital Marketing – Now a Days” for more information on digital marketing. It is also very important to get better command on Google Ads management.
FAQs
- What sets Social Commerce apart from traditional e-commerce? Social Commerce leverages social media platforms to create interactive and engaging shopping experiences, blurring the lines between browsing and buying.
- How can small businesses benefit from Social Commerce? Social Commerce provides small businesses with a level playing field to reach a wider audience and build brand loyalty through authentic interactions.
- Are there any limitations to Social Commerce’s growth? While Social Commerce is on the rise, it may face regulatory challenges and the need to balance monetization with user experience.
- Can Social Commerce benefit B2B businesses as well? Absolutely. B2B businesses can use Social Commerce to showcase their products, share industry insights, and engage with potential clients.
- What skills are essential for a successful Social Commerce strategy? Effective content creation, influencer partnerships, data analysis, and a deep understanding of consumer behavior are key skills for success in Social Commerce.
- What is the new term of ghost commerce? In this regard see the article on ghost commerce.